This webinar features several useful tools to simplify or even eliminate the sample preparation involved prior to mass spectrometry. In this educational session you will learn about several prep-free mass spec techniques that are available, and how to select which method is best for your analysis. Advion will share their perspectives on some of the new tools and protocols to minimize and simplify sample preparation. You’ll learn how to reduce your time in the lab and see your mass spec results in as little as 30 seconds!
As an attendee, you will learn more about:
- How to select the best tools for sample introduction based on your compound
- How new tools can reduce or eliminate sample preparation for results in <30 seconds
- New workflows to maximize your time in the lab by simplifying complex processes
This webinar was presented at the 2023 LabXpo Virtual event by Lab Manager and LabX, recorded July 20, 2023.
Authors: USDA-Agricultural Research Service, Agios Pharmaceuticals, TIC Gums, United States; Universidade Federal de Lavras, Brazil
Abstract
Ethanol extract of cell mass of Serratia marcescens strain N4-5, when applied as a treatment to cucumber seed, has been shown to provide control of the oomycete soil-borne plant pathogen Pythium ultimum equivalent to that provided by a seed-treatment chemical pesticide in some soils. Two dominant compounds in this extract, prodigiosin and the serratamolide serrawetin W1, were identified based on mass and collision induced dissociation mass fragmentation spectra. An additional four compounds with M+H+ masses (487, 541, 543, and 571) consistent with serratamolides reported in the literature were also detected. Several other compounds with M+H+ masses of 488, 536, 684, 834, 906, and 908 m/z were detected in this ethanol extract inconsistently over multiple liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS–MS) runs. A purified preparation of prodigiosin provided control of damping-off of cucumber caused by P. ultimum when applied as a seed treatment while ethanol extract of cell mass of strain Tn246, a transposon-mutant-derivative of strain N4-5, did not. Strain Tn246 contained a mini-Tn5 Km insertion in a prodigiosin biosynthetic gene and was deficient in production of prodigiosin. All other compounds detected in N4-5 extract were detected in the Tn246 extract. This is the first report demonstrating that prodigiosin can control a plant disease. Other compounds in ethanol extract of strain N4-5 may contribute to disease control.
TLC/MS characterization of prodigiosin was performed using the Advion Interchim Scientific® Plate Express™ Automated TLC Plate Reader and expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
With over 20 years of mass spectrometry and chemistry expertise, Advion Interchim Scientific® has produced a family of compact mass spectrometers designed for the chemist. The affordability, small size and ease of use make them ideal for use directly at the chemist’s bench, giving immediate answers and informed decisions instead of waiting.
The Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® compact mass spectrometer (CMS) is a fast and easy analytical tool for the organic chemist. Ideal for fast reaction monitoring, the expression® CMS features a single quadrupole that can adapt to multiple ionization sources in seconds, including both ESI and APCI. The mass spectrometer works in a variety of applications, including food and beverage, pharmaceutical, biomedical, peptides and proteins, drug discovery and more. The expression® CMS offers a variety of novel sampling techniques, including:
- Direct mass analysis of TLC plates in 30 seconds at the push of a button with Plate Express®
- One-touch analysis of solids and liquid samples with the ASAP® probe
- LC/CMS
- Many more options and configurations to suit your needs
Learn more about the different sample techniques available with the expression® CMS, including fast assay methods for liquids, solids, gases, and even air-sensitive compounds.
Fill out the form to download the full expression® CMS brochure now.
Authors: Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research, Germany; University of Twente, Netherlands
Abstract
We developed a simple way to create 2D conductive nanostructures with dielectric cores and conductive surfaces based on polyethylene with in-chain thiophene groups. Generally, thiophene-based polymers show great conductive properties, but exhibit a poor processability. Here, we use the crystallization of a polyethylene chain with precisely distributed thiophene groups as the platform for a self-organization of a lamellar structure. During crystallization, thiophene groups are expelled to the crystal surface. Subsequent copolymerization with 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) molecules finally yields 2D platelets with a conductive surface. The electric properties of the surface are demonstrated by conductivity measurements. Given the molecular structure of the polymer, it can be assumed that the conductive layer consists of only one monoatomic layer of polymerized thiophene. We thus show a new way to create an ultra-thin, conductive surface on a polymer surface in just a few steps. Hence, the method presented here opens up a wide range of possibilities to produce complex, nanoscale electronic structures for microelectronic applications.
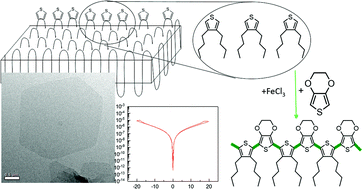
Mass spectrum analysis was obtained by ASAP/CMS using the Advion Interchim Scientific® ASAP® Atmospheric Solids Analysis Probe and expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS)
AstraZeneca, United Kingdom
Abstract
Deuterium exchange has been demonstrated to provide additional information to accurate mass measurement and collision‐induced dissociation on unknown chemical structures. An enhanced method for rapid deuterium exchange could make this technique more routine for structural elucidation. Open port sampling interface mass spectrometry (OPSI‐MS) with an aprotic solvent offers a rapid method for performing deuterium incorporation.
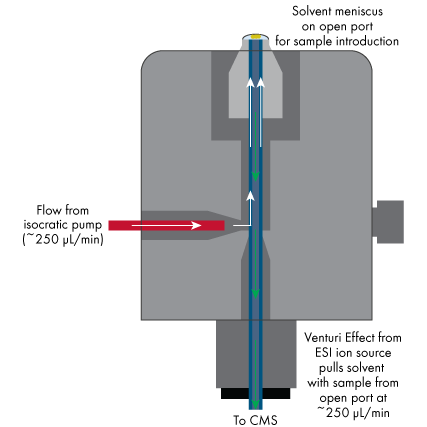
This publication features the Advion Interchim Scientific® Touch Express™ OPSI with the expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Institute of Food Research, Genome Analysis Center, Aix-Marseille University, University of East Anglia
Abstract
We previously identified and characterized an intramolecular trans-sialidase (IT-sialidase) in the gut symbiont Ruminococcus gnavus ATCC 29149, which is associated to the ability of the strain to grow on mucins. In this work we have obtained and analyzed the draft genome sequence of another R. gnavusmucin-degrader, ATCC 35913, isolated from a healthy individual. Transcriptomics analyses of both ATCC 29149 and ATCC 35913 strains confirmed that the strategy utilized by R. gnavus for mucin-degradation is focused on the utilization of terminal mucin glycans. R. gnavus ATCC 35913 also encodes a predicted IT-sialidase and harbors a Nan cluster dedicated to sialic acid utilization. We showed that the Nan cluster was upregulated when the strains were grown in presence of mucin. In addition we demonstrated that both R. gnavus strains were able to grow on 2,7-anyhydro-Neu5Ac, the IT-sialidase transglycosylation product, as a sole carbon source. Taken together these data further support the hypothesis that IT-sialidase expressing gut microbes, provide commensal bacteria such as R. gnavus with a nutritional competitive advantage, by accessing and transforming a source of nutrient to their own benefit.
Mass spectrometry analysis was performed on the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) and the data was evaluated using Advion Interchim Scientific® Data Express software.
USDA, University of Connecticut
Abstract
Research methods that predict Fe bioavailability for humans can be extremely useful in evaluating food fortification strategies, developing Fe-biofortified enhanced staple food crops and assessing the Fe bioavailability of meal plans that include such crops. In this review, research from four recent poultry (Gallus gallus) feeding trials coupled with in vitro analyses of Fe-biofortified crops will be compared to the parallel human efficacy studies which used the same varieties and harvests of the Fe-biofortified crops. Similar to the human studies, these trials were aimed to assess the potential effects of regular consumption of these enhanced staple crops on maintenance or improvement of iron status. The results demonstrate a strong agreement between the in vitro/in vivo screening approach and the parallel human studies.
LC/MS analysis was complete using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS). Instrumentation and data acquisition were controlled by Advion Mass Express software
University of Florida, USDA, Kansas State University
Abstract
Currently, the global citrus production is declining due to the spread of Huanglongbing (HLB). HLB, otherwise known as citrus greening, is caused by Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus (CLas) and is transmitted by the Asian citrus psyllids (ACP), Diaphorina citri Kuwayama.
In this study, we investigated the micro- and macro-nutrients, nucleotides, and others secondary metabolites of phloem sap from pineapple sweet orange. The micro- and macro-nutrients were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS) and inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). Nucleotides and other secondary metabolites analysis was accomplished by reversed phase HPLC coupled with UV, fluorescence detection, or negative mode electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Gujarat University
Abstract
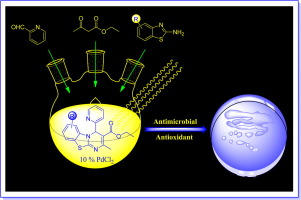
Synthesis of new and desired compounds has an everlasting demand. The present work emphasizes on the one pot, three component microwave assisted synthesis of novel ethyl 2-methyl-4-(pyridin-2-yl)-4H-benzo[4,5]thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylate derivatives by the reaction of 2-aminobenzothiazole derivatives with Pyridine 2-aldehyde and Ethyl acetoacetate in the presence of PdCl2 as an expeditious catalyst under solvent-free condition.
The salient features of this approach are operational simplicity, convergence, short reaction time, high atom economy, easy workup, mild reaction conditions and environmentally benign conditions. All the newly synthesized diverse poly-functionalized tri-heterocyclic benzothiazole derivatives have been characterized by elemental analysis and various spectroscopic methods such as FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, ESI-MS and Single crystal X-ray analysis (4a). All the final scaffolds have been screened for antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Also their antitubercular activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37RV was screened.
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) analysis was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Gujarat University
Abstract
A concise, facile and straightforward synthetic protocol has been described for the preparation of 6-amino-1,4-dihydropyrano[2,3-c]-pyrazole-5-carbonitrile derivatives by a one-pot, three-component reaction of ethyl acetoacetate, hydrazine hydrate, aryl aldehydes and malononitrile in glycerol as a green and reusable reaction media under catalyst free condition. The corresponding 6-amino-1,4-dihydropyrano[2,3-c]-pyrazole-5-carbonitriles have been obtained with good to excellent yields (86-92%). This protocol is highly efficient due to its mild reaction conditions, operational simplicity, use of inexpensive, eco-friendly and green reaction media, catalyst-free conditions and absence of toxic organic solvents.
Electrospray mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).



