University of Durham
Abstract
The synthesis of diazonium salts is historically an important transformation extensively utilized in dye manufacture. However the highly reactive nature of the diazonium functionality has additionally led to the development of many new reactions including several carbon-carbon bond forming processes. It is therefore highly desirable to determine optimum conditions for the formation of diazonium compounds utilizing the latest processing tools such as flow chemistry to take advantage of the increased safety and continuous manufacturing capabilities. Herein we report a series of flow-based procedures to prepare diazonium salts for subsequent in-situ consumption.
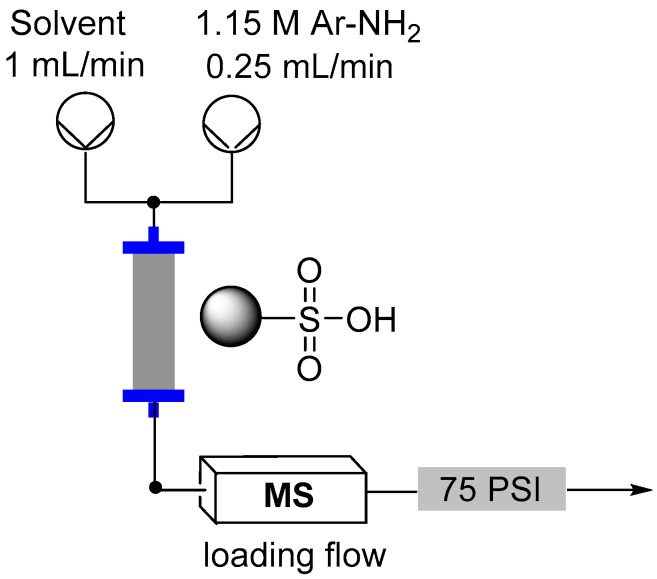
Flow reactor loading set-up.
Direct in-line mass spec analysis was performed using the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) with electrospray ionization (ESI).
Western Washington University
Abstract
Sortase‐catalyzed transacylation reactions are widely used for the construction of non‐natural protein derivatives. However, the most commonly used enzyme for these strategies (sortase A from Staphylococcus aureus) is limited by its narrow substrate scope. To expand the range of substrates compatible with sortase‐mediated reactions, we characterized the in vitro substrate preferences of eight sortase A homologues.
From these studies, we identified sortase A enzymes that recognize multiple substrates that are unreactive toward sortase A from S. aureus.
We further exploited the ability of sortase A from Streptococcus pneumoniae to recognize an LPATS substrate to perform a site‐specific modification of the N‐terminal serine residue in the naturally occurring antimicrobial peptide DCD‐1L.
Finally, we unexpectedly observed that certain substrates (LPATXG, X=Nle, Leu, Phe, Tyr) were susceptible to transacylation at alternative sites within the substrate motif, and sortase A from S. pneumoniae was capable of forming oligomers. Overall, this work provides a foundation for the further development of sortase enzymes for use in protein modification.
Mass spectrometry analysis was performed using the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Nirma University, India; Rega Institute for Medical Research
Abstract
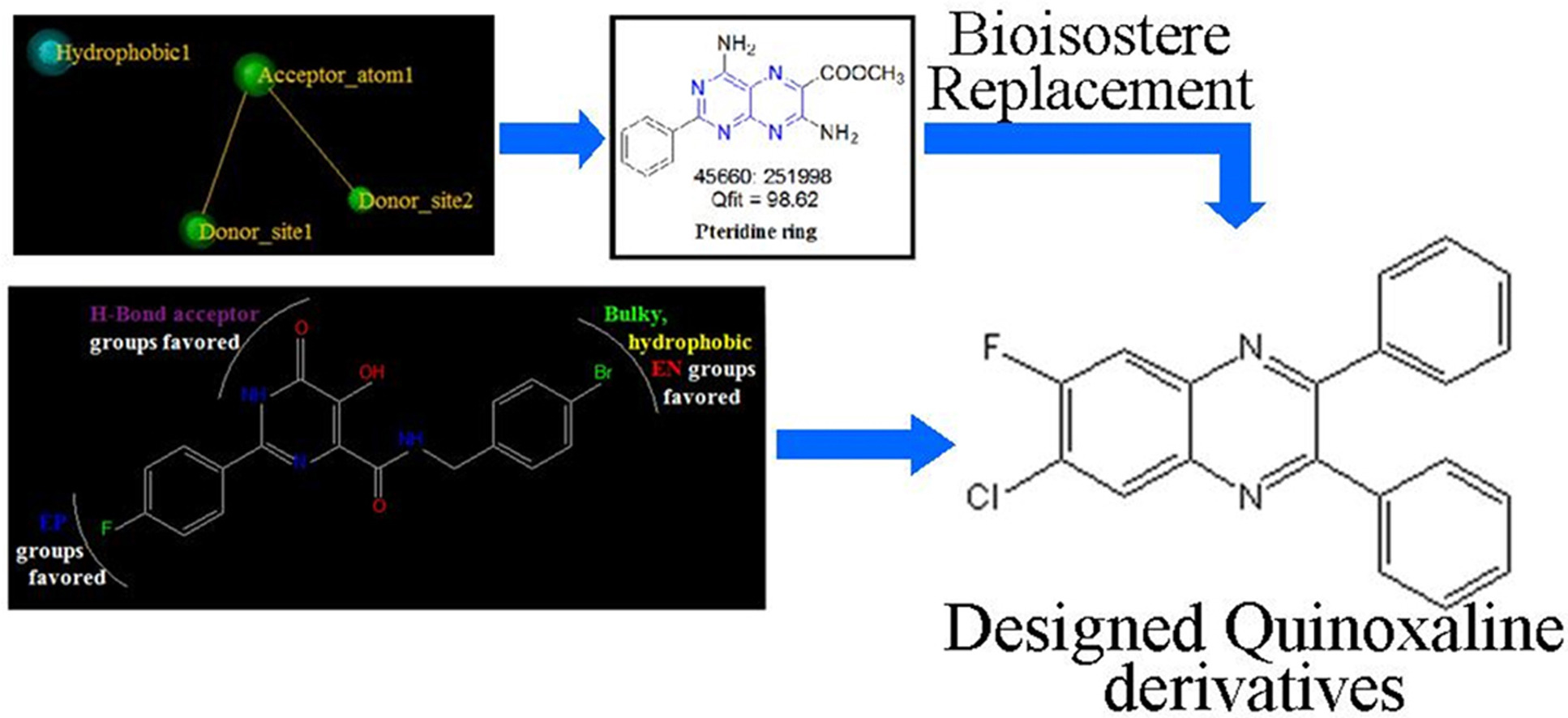
In order to design novel anti-HIV agents, pharmacophore modelling, virtual screening, 3D-QSAR and molecular docking studies were performed. 50 quinoxaline derivatives with different substitutions were designed on basis of both ligand based drug design approaches and were mapped on the best pharmacophore model. From this, best 32 quinoxaline derivatives were docked onto the active site of integrase enzyme and in-silico ADMET properties were also predicted. From this data, synthesis of top 7 quinoxaline derivatives was carried out and were characterized using Mass, 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectroscopy. Purity of compounds were checked using HPLC.
Two quinoxaline derivatives showed good results, which can be further explored to develop novel anti-HIV agents.
Lyon College, University of Rhode Island
Abstract
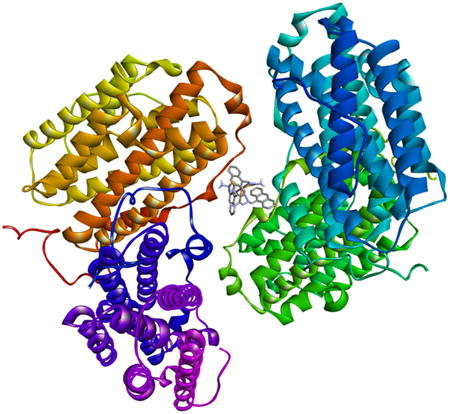
MOLSTR, Accepted manuscript. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.05.075
We have synthesized a trio of gallium complexes bearing 9-anthraldehyde thiosemicarbazones. The complexes were assessed for their anticancer activity and their biophysical reactivity was also investigated.
The results of docking studies with DNA, ribonucleotide reductase and human serum albumin, however showed that the complex with the best biological activity had the largest binding constant to DNA.
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) was recorded using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Xention Limited, United Kingdom; University of Ljubljana, Slovenia
Abstract
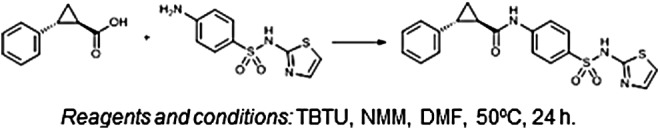
The rodent neuroblastoma cell line, ND7-23, is used to express voltage-dependent sodium (Nav) and other neuronal ion channels resistant to heterologous expression in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells. Their advantage is that they provide endogenous factors and signaling pathways to promote ion channel peptide folding, expression, and function at the cell surface and are also amenable to automated patch clamping. However, ND7-23 cells exhibit endogenous tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive Nav currents, and molecular profiling has revealed the presence of Nav1.2, Nav1.3, Nav1.6, and Nav1.7 transcripts, but no study has determined which subtypes contribute to functional channels at the cell surface. In this publication, we profiled the repertoire of functional Nav channels endogenously expressed in ND7-23 cells using the QPatch automated patch clamp platform and selective toxins and small molecules.
Mass spec analysis was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Mokpo National University, Gachon University, Hanyang University, Gachon Medical Research Institute, South Korea; University of Bremen, Germany
Abstract
G protein-coupled receptor (GPR) 119 is expressed in pancreatic β-cells and intestinal L cells, and is involved in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) release, respectively. Therefore, the development of GPR119 agonists is a potential treatment for type 2 diabetes. In this publication, screened 1500 natural plant extracts for GPR119 agonistic actions and investigated the most promising extract, that from Angelica dahurica (AD), for hypoglycemic actions in vitro and in vivo.
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) data was measured using the Advion expression CMS
Gujarat University
Abstract
A library of thiosemicarbazide hybrid 2-(aldo-polyhydroxyalkyl)benzimidazole derivatives have been designed and synthesized with simple and eco-friendly methodologies. The structures of the compounds have been elucidated with the aid of elemental analysis, IR, mass and 1H NMR spectral data. These novel synthesized compounds have been evaluated for their antibacterial activity against two gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus and S. pyogenus) and two gram-negative bacteria (P. aeruginosa and E. coli). The title compounds have also been studied for their antifungal activity against C. albicans, A. niger and A. clavatus using the broth dilution technique.
Mass spec analysis was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) with electrospray ionization (ESI).
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
Abstract
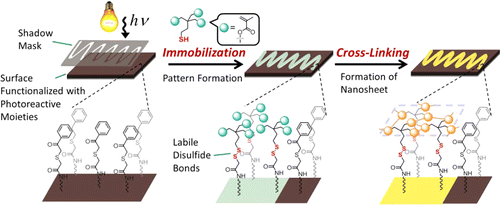
The preparation of cross-linked nanosheets with 1–2 nm thickness and predefined shape was achieved by lithographic immobilization of trimethacryloyl thioalkanoates onto the surface of Si wafers, which were functionalized with 2-(phenacylthio)acetamido groups via a photoinduced reaction. Subsequent cross-linking via free radical polymerization as well as a phototriggered Diels–Alder reaction under mild conditions on the surface led to the desired nanosheets. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS), as well as infrared reflection-absorption spectroscopy (IRRAS) confirmed the success of individual surface-modification and cross-linking reactions.
ESI-MS analysis was performed using the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Gujarat University
Abstract
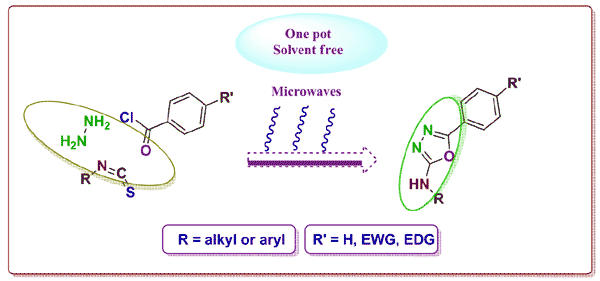
A convenient one-pot, multi-component and solvent free procedure for the preparation of substituted 2-amino-5-aryl-1,3,4-oxadiazoles has been achieved. The method is a significant improvement over previously reported synthesis. Reaction of acid chlorides with hydrazine hydrate and isothiocynates under microwave-irradiation (MWI) afforded the corresponding 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives in high yields with high purity. All synthesized compounds were characterized by FT-IR, proton and carbon NMR, mass spectroscopy and elemental analysis. A possible mechanism is proposed for the cyclodesulfurization based on the results of this study.
Mass spec analysis was performed on the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) using electrospray ionization (ESI).
Guru Ghasidas University, University of South Dakota
A one-pot practical, efficient, and environmentally benign multicomponent synthesis of 4H-pyrans and polysubstituted aniline derivatives of biological, pharmacological, and optical applications has been developed using a very mild, neutral, and reusable silica nanoparticles as catalyst. The 4H-pyran derivatives were synthesized by a three component reaction of an aldehyde, malononitrile, and 5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione or ethyl acetoacetate at room temperature or refluxing in ethanol. Alternatively, polysubstituted anilines were synthesized via a four component reaction of an aldehyde, a ketone, and two equivalents of malononitrile in ethanol.
Mass spec analysis was carried out using an Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).






